An online chiller is a highly responsive, self-contained cooling unit designed to deliver continuous, precise, and on-demand cooling to industrial processes. Unlike traditional chillers that operate based on storage capacity or intermittent duty cycles, online chillers function in a real-time loop, immediately reacting to fluctuations in load, temperature, or system demands.
Used in fields such as laser technology, medical imaging, CNC machining, food-grade packaging, plastics, and electronics cooling, these systems are vital where even a few seconds of temperature deviation can compromise product quality or equipment safety.
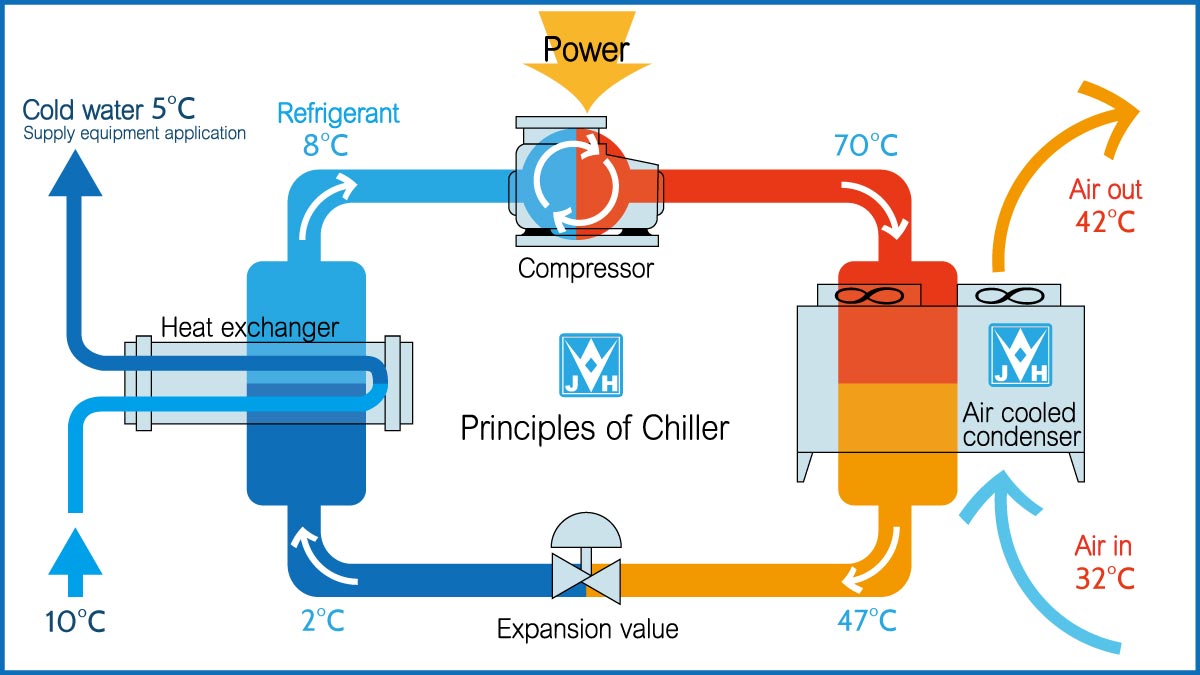
The mechanism of an online chiller revolves around the refrigeration cycle, where refrigerant circulates through four main stages — evaporation, compression, condensation, and expansion — all regulated by an intelligent control system.
Detailed Working Mechanism of Online Chiller
Evaporation – Where the Heat is Captured
- Component: Evaporator (usually a shell-and-tube or brazed plate heat exchanger).
- Process:
- Warm process water or coolant enters the evaporator.
- The low-pressure refrigerant absorbs heat from the fluid and begins to boil.
- This phase change from liquid to vapor draws out thermal energy.
- Result: The fluid exits cooled, and the refrigerant becomes a low-pressure vapor.
Real-World Application: In a laser cutting operation, this step removes heat generated by the laser head to prevent overheating and maintain precision.
Compression – Energy is Added to the Vapor
- Component: Compressor (scroll, screw, or reciprocating).
- Process:
- The refrigerant vapor is sucked into the compressor.
- It is compressed to a higher pressure and temperature, preparing it for heat rejection.
- Result: High-pressure, high-temperature vapor ready for condensation.
Online Chiller Insight: Scroll compressors are often preferred for their quiet operation and compact design, while screw compressors are used in higher-capacity online chillers.
Condensation – Heat is Released
- Component: Condenser coil (air-cooled or water-cooled).
- Process:
- The hot vapor flows through the condenser.
- Ambient air (via fan) or cooling water absorbs and removes heat.
- The refrigerant condenses into a high-pressure liquid.
- Result: Heat is expelled from the chiller, and the refrigerant is ready to cycle back.
Modern Innovation: Microchannel or finned-tube condensers enhance efficiency in compact online chillers used in limited-space environments.
Expansion – Pressure and Temperature Drop
- Component: Expansion Valve (typically an Electronic Expansion Valve or Thermostatic Expansion Valve).
- Process:
- The high-pressure liquid refrigerant flows through the valve.
- The valve creates a sudden pressure drop.
- The refrigerant becomes a low-pressure, low-temperature mixture.
- Result: The refrigerant is ready to enter the evaporator and absorb more heat.
Unique Feature in Online Chillers: Electronic expansion valves respond instantly to sensor data, providing tight control over flow and improving part-load efficiency.
Control System – The Intelligent Brain
- Component: Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) or microcontroller-based system.
- Process:
- Continuously monitors temperature, pressure, flow, and ambient conditions.
- Regulates compressor speed, fan operation, expansion valve opening, and alarms.
- Responds instantly to changes in thermal load.
- Result: Seamless, automated temperature control within ±0.5°C accuracy.
Advanced Feature: Many online chillers now offer IoT-based remote monitoring, fault prediction alerts, and cloud diagnostics for 24/7 operational oversight.
Special Features in Online Chiller Working
Real-Time Load Matching
- System adjusts operation based on instant demand, not fixed cycle logic.
- Results in energy-efficient operation and reduced wear.
Adaptive Safety Controls
- Monitors:
- High/low pressure,
- Over-temperature,
- Flow errors,
- Compressor overloads.
- Shuts down or throttles back based on preset logic to prevent component damage.
Closed-Loop vs. Open-Loop Cooling
- Closed-loop: Chilled fluid is recycled continuously — ideal for sensitive equipment.
- Open-loop: Water enters once, absorbs heat, and exits — suitable for rugged industrial use.
The working mechanism of an online chiller is an elegant orchestration of thermodynamics and digital intelligence. It transforms ambient conditions into tightly regulated process temperatures using a closed-loop refrigerant system, bolstered by automated controls, real-time feedback loops, and smart diagnostics.
Online chillers not only remove heat — they respond to it, adapt to it, and optimize around it. This ability to deliver precision cooling on demand makes them indispensable in today’s high-performance, energy-conscious industries.
Understanding this mechanism helps industries select the right model, ensure proper integration, and reduce operating costs, while maintaining top-tier process reliability.